Sub Categories
There are a variety of liquid cooling methods to manage heat. The following are some of the most common that Wakefield Thermal offers.
Liquid Cold Plates:
The most common method to accomplish liquid cooling is to have a plate with a flow path that moves liquid under the devices. After the heat is absorbed into the liquid, it is taken out of the plate and into the larger system. While water or water/glycol are the most common fluids used in liquid cooling, gasoline, oil, and refrigerant are other fluids that can be utilized.
There are various methods of construction which can be used on liquid cold plates to minimize the strain of the pump and still achieve the required thermal performance. These methods of construction are evaluated by the Wakefield Thermal engineers in an effort to find the minimal cost that still meets the required performance.
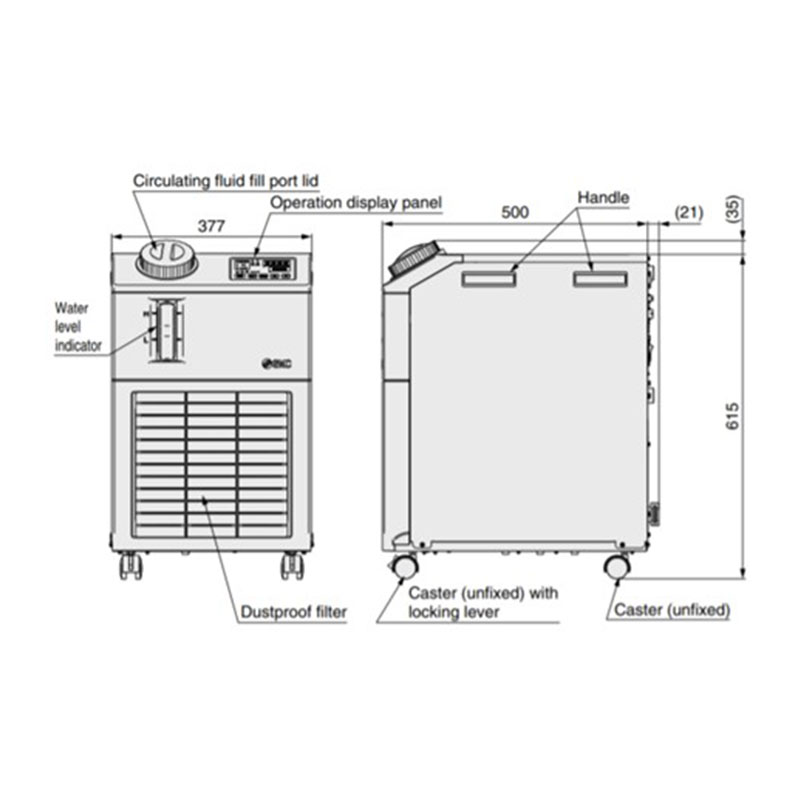
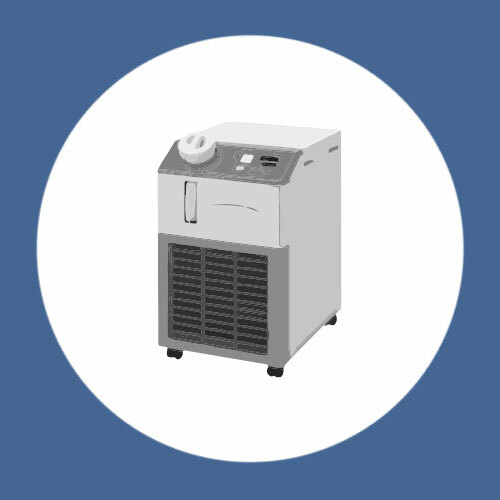
High Performance Liquid Chillers:
Liquid chillers feature a circulating fluid temperature controller with both air cooled and water cooled options. Compact and easily transported to and from work sites, the chillers are ideal for applications like laser mining, UV curing devices, X-ray instruments, temperature control of paint material, and more.
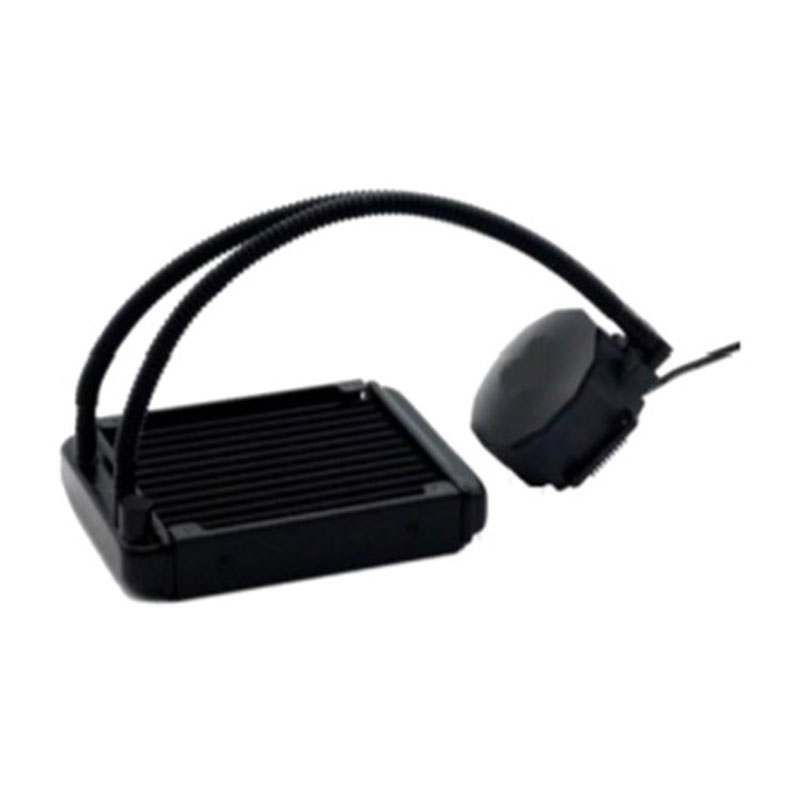
CPU Liquid Coolers:
Wakefield Thermal's RAPID Liquid CPU cooler is a device designed to draw heat away from the system CPU and other components in an enclosure. Using a Liquid CPU cooler to lower CPU temperatures improves efficiency and stability of the system more than a forced fan convection device.
The CDU controller provides intelligent monitoring and interfaces with building management systems and web management tools for the highest reliability.

 US Dollars
US Dollars





